
A vulnerability to events that impact broad economic outcomes is called systematic risk. These outcomes include aggregate earnings, total resource holdings, as well market returns. As such, systematic risk varies widely from one country to another. There are three main types of systematic risks. These are market and inflation risks, as well as negative externalities. Let's go over each one. Consider how systematic risks can affect your portfolio and investments.
Market risk
Systematic risk, also known as market risk, is a risk that investors face when investing in stocks and bonds. It is caused by changes in the price of the underlying assets, including the underlying market itself. This risk is often magnified by large investors who hold large amounts of securities. Investors are also exposed to credit and business risk. These risks refer to uncertainty about a company's creditworthiness or prospects.
Inflation risk
Inflation can be a serious risk to a person's financial security. Inflation decreases the purchasing power and prices rise. Fixed income investments such bonds with a fixed interest and high purchasing power are especially vulnerable to inflation. Fortunately, there are various financial tools investors can use to mitigate the risks associated with inflation. Here are some common ones. -Inflation periods are a good time to increase your income in order to reduce systematic risk

Purchasing power risk
A type of systematic risk called purchasing power risk or inflation risk is when your investment portfolio can lose its value. This is because inflation reduces money's purchasing power. This means that the same amount money can buy fewer goods and services. This can make it difficult to spend your money. Fixed income securities are especially vulnerable because their investments are valued in nominal terms. Equity shares, however, are less susceptible to purchasing power risks.
Negative externalities
There are many examples in economics of negative externalities. Light pollution is just one example. There is no way for the affected to be compensated if street lights are on. The environmental impact of production or consumption is another example. One example is that the cost of manufacturing products can create noise that is disruptive to nearby residents. Consumers don't have to compensate for this noise. Both production and consumption have significant negative externalities.
Increasing capital
There is a positive correlation among the firm's expected returns and the amount of capital it takes. If the firm has too little risk capital, however, this correlation can be negative. Capital requirements can lead to bank stocks being valued lower. These effects cannot be avoided. Policymakers should consider other policy options, in addition to raising capital requirements, to avoid these negative consequences. This paper examines two main policy options.
Diversification
As the name suggests, diversification is a way to manage systematic risk, as well as unsystematic risk. Systematic risk can be described as an undistributed stock market risk. Unlike unsystematic risk, which can affect the entire market, systematic risk is limited to one specific security or portfolio. Diversifying can help minimize systematic risks. Diversification reduces systemic risk by narrowing the range of possible outcomes and increasing the diversity within a portfolio.
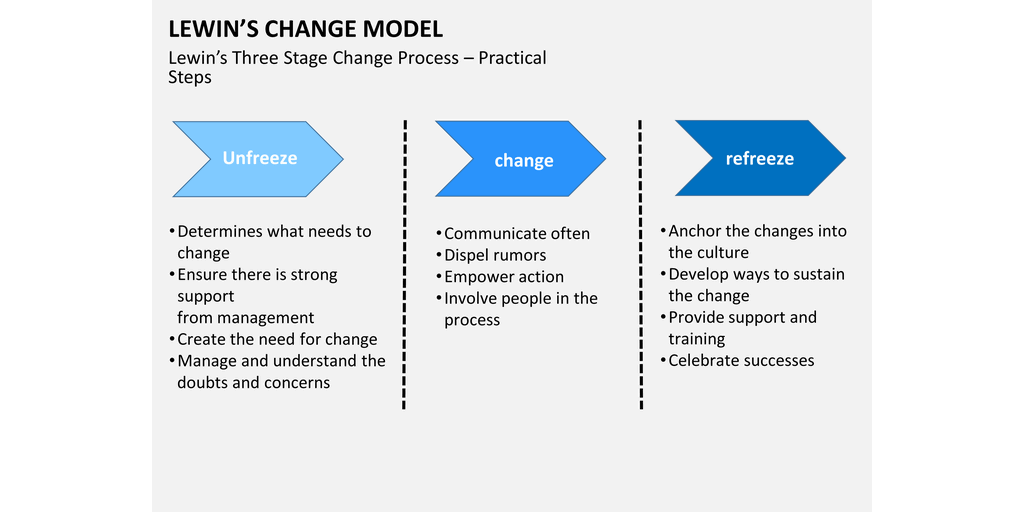
Measurement
Systematic risk is the potential for financial system failures due to the characteristics of the financial system. Its enormous costs make efficient macroprudential regulation of financial institutions imperative. This paper proposes a new way to assess systemic risk. This analysis will be especially useful to policymakers who seek stability and cost-effectiveness in their financial systems. The methodology is based in statistical methods and can apply to any type or financial system.
FAQ
What are the three main management styles you can use?
There are three types of management: participative, laissez faire, and authoritarian. Each style has strengths and flaws. What style do you prefer? Why?
Authority - The leader is the one who sets the direction and expects everyone in the organization to follow it. This style works well if an organization is large and stable.
Laissez faire - Each individual can decide for himself/herself. This style works best when an organization is small and dynamic.
Participative - Leaders listen to all ideas and suggestions. This style is most effective in smaller organizations, where everyone feels valued.
What is TQM exactly?
The industrial revolution saw the realization that prices alone were not sufficient to sustain manufacturing companies. This led to the birth of quality. They had to improve efficiency and quality if they were to remain competitive.
To address this need for improvement management created Total Quality Management (TQM) which aimed to improve all aspects of an organization's performance. It included continuous improvement, employee involvement and customer satisfaction.
Six Sigma is so well-known.
Six Sigma can be implemented quickly and produce impressive results. Six Sigma also gives companies a framework for measuring improvement and helps them focus on what is most important.
What are some common mistakes managers make?
Sometimes managers make it harder for their employees than is necessary.
They may not assign enough responsibilities to staff members and provide them with inadequate support.
Managers often lack the communication skills necessary to motivate and guide their teams.
Managers set unrealistic expectations and make it difficult for their team.
Managers may choose to solve every problem all by themselves, instead of delegating to others.
What role should a manager play within a company
The role of a manager varies from one industry to another.
A manager generally manages the day to-day operations in a company.
He/she makes sure that the company meets its financial obligations, and that it produces goods or services that customers desire.
He/she ensures that employees follow the rules and regulations and adhere to quality standards.
He/she oversees marketing campaigns and plans new products.
What is the main difference between Six Sigma Six Sigma TQM and Six Sigma Six Sigma?
The main difference between these two quality management tools is that six sigma focuses on eliminating defects while total quality management (TQM) focuses on improving processes and reducing costs.
Six Sigma is a method for continuous improvement. This approach emphasizes eliminating defects through statistical methods like control charts, Pareto analysis, and p-charts.
This method has the goal to reduce variation of product output. This is done by identifying root causes and rectifying them.
Total quality management involves measuring and monitoring all aspects of the organization. It also includes training employees to improve performance.
It is used to increase productivity.
How do you manage employees effectively?
Effectively managing employees requires that you ensure their happiness and productivity.
It means setting clear expectations for them and keeping an eye on their performance.
Managers need clear goals to be able to accomplish this.
They should communicate clearly with employees. They need to communicate clearly with their staff.
They must also keep track of the activities of their team. These include:
-
What did we accomplish?
-
How much work was done?
-
Who did it?
-
What was the moment it was completed?
-
Why did it happen?
This information can be used for monitoring performance and evaluating results.
Statistics
- The average salary for financial advisors in 2021 is around $60,000 per year, with the top 10% of the profession making more than $111,000 per year. (wgu.edu)
- Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees (upcounsel.com)
- UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers on its site. (upcounsel.com)
- 100% of the courses are offered online, and no campus visits are required — a big time-saver for you. (online.uc.edu)
- This field is expected to grow about 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average for job growth. (wgu.edu)
External Links
How To
How do I get my Six Sigma certification?
Six Sigma is a tool for quality management to improve processes and increase efficiency. It is a process that helps businesses achieve consistent results in their operations. The name is derived from the Greek word "sigmas", which means "six". Motorola created this process in 1986. Motorola realized that standardizing manufacturing processes was necessary to make products more efficient and less expensive. Because of the number of people involved in the work, they had problems maintaining consistency. To resolve this issue, they used statistical tools like Pareto analysis and control charts. They would then apply these techniques to all aspects of their operation. After applying the technique, they could make improvements wherever there was potential. The Six Sigma certification process involves three major steps. To determine whether you are qualified, the first step is to verify your eligibility. Before you can take any tests, you will need to take some classes. After you have passed the classes, you can start taking the exams. You will want to remember everything you learned in the class. Next, you'll be ready for the test. If you pass, your certification will be granted. Finally, you can add your certifications on to your resume.